A two-component therapy for adults with late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD) weighing 88 lbs or more who are not improving on their current enzyme replacement therapy (ERT).

Education+Actiona more informed you
LOPD is a rare that causes muscle weakness
People with LOPD are deficient in a certain type of enzyme, called . The GAA enzyme is responsible for breaking down into glucose.
When excess builds up in the , it causes damage to the muscles throughout the body. This leads to mobility problems and respiratory issues as the muscles responsible for movement and breathing begin to break down.
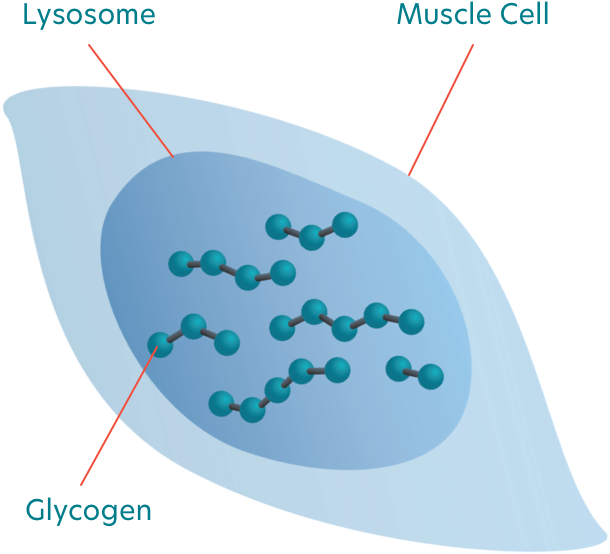
What causes Pompe disease?
Pompe is a genetic disease caused by mutations of the GAA gene. For a person to have Pompe disease, GAA mutations must be inherited from both parents. If 1 of the 2 inherited GAA genes is normal, a person will not have Pompe disease, but would be considered a “carrier”—meaning they may pass the mutation to their children.
What is late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD)?
LOPD causes symptoms that may not be noticeable at first and can mimic other disorders. People with Pompe disease have low levels of activity, which limits their body’s ability to break down glycogen. Due to the damage this glycogen buildup may cause to the muscles involved in walking and breathing, some people with LOPD eventually require the use of assistive devices.
In individuals with LOPD, activity can typically range anywhere from 2% to 40% of what’s considered normal. Because of this wide range, the amount of activity each person has can generally impact the severity and progression of their disease.
Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) replaces the natural GAA that people with LOPD lack. But it can become vulnerable and lose function once infused into the bloodstream.
LOPD can take up to 10 years to diagnose
LOPD is difficult to diagnose and often misdiagnosed, in part because it’s a rare disease, but also because its symptoms can often feel disconnected and mistaken for other conditions. This can result in a long and frustrating diagnostic journey.
LOPD treatment challenges
When ERT is infused into the blood, it can lose its shape and function. As a result, only a fraction of active ERT is available. The next challenge is that ERT must bind to and enter the muscle cells to be processed into its most active form to break down excess glycogen.
Many people who received ERT (alglucosidase alfa) began experiencing declines 3-5 years after starting treatment.



“Once I was diagnosed, it was really important to start thinking about treatment and disease management options.”
— Maddie on the importance of creating a
treatment plan with her medical care team

PREP FOR YOUR NEXT APPOINTMENT
Discover a tool that helps you track how you're feeling and gets you ready for a conversation with your doctor
Learn how it may help
Explore the impact that POMBILITI + OPFOLDA had on walking distance and breathing function in adults previously treated with ERT, and review the clinical trial safety data.
Important Safety Information
POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA may cause serious side effects, including:
- Hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis): Severe and potentially life-threatening allergic-type reactions related to the infusion may occur during and after POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA treatment. Your doctor will inform you of the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions which may include: difficulty breathing or swallowing, rash or hives, low blood pressure, swelling of lips, tongue, throat or face. Seek medical care immediately should signs and symptoms occur. If a severe reaction occurs, your doctor may decide to immediately discontinue the infusion and provide medical care. Appropriate medical support measures may be administered, and you may require close observation during and after POMBILITI infusion.
What are POMBILITI and OPFOLDA?
POMBILITI and OPFOLDA are prescription medicines used in combination for the treatment of adults with late-onset Pompe disease weighing 88 pounds (40 kg) or more and who are not improving on their current enzyme replacement therapy (ERT).
It is not known if POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA is safe and effective in children with late-onset Pompe disease.
Important safety information
POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA may cause serious side effects, including:
- Hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis): Severe and potentially life-threatening allergic-type reactions related to the infusion have been reported during and after POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA treatment. Your doctor will inform you of the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions which may include: difficulty breathing or swallowing; rash or hives; low blood pressure; swelling of lips, tongue, throat, or face. Seek medical care immediately should signs and symptoms occur. If a severe reaction occurs, your doctor may decide to immediately discontinue the infusion and provide medical care. Appropriate medical support measures may be administered, and you may require close observation during and after POMBILITI infusion.
- Infusion-Associated Reactions (IARs): Severe IARs related to the infusion have been reported during or after POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA. Your doctor will inform you of the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions which may include: hives, itching, shortness of breath, flushing, chills, and low blood pressure. Seek medical care immediately should signs and symptoms occur. If severe IARs occur during infusion, your doctor may decide to immediately discontinue the infusion and provide appropriate medical care. If you have an acute underlying illness at the time of POMBILITI infusion you may be at greater risk for IARs. If you have advanced Pompe disease you may have compromised heart and breathing function, which may put you at a higher risk of severe complications from IARs.
- Risk of Acute Cardiorespiratory Failure: If you are likely to develop fluid volume overload or have an acute breathing condition or heart and/or breathing problems that require fluid restriction, you may be at risk of worsening of your heart or breathing status during POMBILITI infusion. Your doctor may decide that close observation during and after POMBILITI administration may be necessary.
Do not take POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA if you are pregnant.
Before taking POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have kidney problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA may cause harm to your unborn baby.Females who are able to become pregnant:
- Your healthcare provider will check if you are pregnant before you start treatment with POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA.
- You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA and for at least 60 days after the last dose.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you might be pregnant during treatment with POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if OPFOLDA alone or in combination with POMBILITI passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during this time.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
POMBILITI and OPFOLDA must be taken in combination. POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA will be given to you 1 time every other week.
The most common side effects of POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA include: headache, diarrhea, tiredness, nausea, stomach area pain, and fever.
POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA may cause fertility problems in females and males, which may affect the ability to have children. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have concerns about fertility.
These are not all the possible side effects of POMBILITI and OPFOLDA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
What are POMBILITI and OPFOLDA?
POMBILITI and OPFOLDA are prescription medicines used in combination for the treatment of adults with late-onset Pompe disease weighing 88 pounds (40 kg) or more and who are not improving on their current enzyme replacement therapy (ERT).
It is not known if POMBILITI in combination with OPFOLDA is safe and effective in children with late-onset Pompe disease.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING, for POMBILITI and full Prescribing Information and Patient Information for OPFOLDA.

